Case Studies: Recognizing And Managing Agonal Rhythms In Practice
Case Studies: Recognizing And Managing Agonal Rhythms In Practice. Discover more detailed and exciting information on our website. Click the link below to start your adventure: Visit Best Website. Don't miss out!
Table of Contents
Case Studies: Recognizing and Managing Agonal Rhythms in Practice
Introduction: Agonal rhythms represent a critical juncture in patient care, often preceding cardiac arrest. For healthcare professionals, particularly those in emergency medicine, critical care, and cardiology, understanding and managing agonal rhythms is paramount. This article presents real-world case studies illustrating the challenges and effective strategies for recognizing and managing these complex arrhythmias. Effective identification and swift intervention are key to improving patient outcomes.
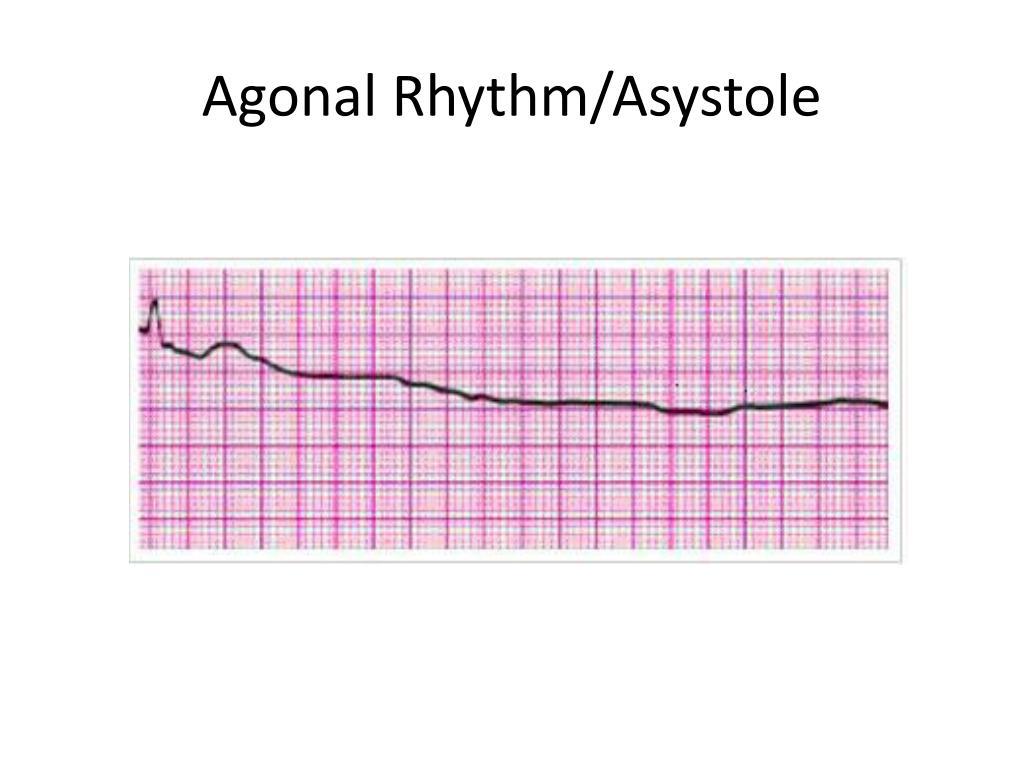
What are Agonal Rhythms?
Agonal rhythms are irregular, often chaotic heart rhythms that occur just before cardiac arrest. They are a terminal sign, indicating the heart's failing ability to effectively pump blood. These rhythms are characterized by:
- Extremely slow heart rates (bradycardia): Often below 20 beats per minute.
- Irregular waveforms: Lacking the typical organized patterns seen in normal heart rhythms.
- Low amplitude: Weak electrical signals, indicating poor myocardial contractility.
- Potential for evolving into asystole: Complete absence of electrical activity.
Recognizing agonal rhythms requires a keen eye and understanding of ECG interpretation. Improper identification can lead to delayed or inappropriate interventions, significantly impacting survival rates.
Case Study 1: The Elderly Patient with Underlying Conditions
A 78-year-old male patient with a history of congestive heart failure and atrial fibrillation presented to the emergency department with sudden onset of shortness of breath and altered mental status. The ECG revealed an agonal rhythm with extremely low amplitude and irregular P waves.
- Challenges: Differentiating agonal rhythm from other bradycardias.
- Interventions: Immediate initiation of CPR, advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) protocols, and emergent intubation. While resuscitation efforts were heroic, the patient ultimately succumbed to the underlying cardiac pathology.
- Lessons Learned: The case highlights the importance of considering underlying comorbidities when interpreting agonal rhythms and underscores the need for rapid intervention even in seemingly hopeless situations.
Case Study 2: The Young Trauma Patient
A 25-year-old female patient arrived after a severe motor vehicle accident. Despite initial stabilization, her ECG showed an agonal rhythm.
- Challenges: Distinguishing agonal rhythm from the effects of trauma-induced hypovolemia and shock.
- Interventions: Aggressive fluid resuscitation, blood transfusions, and continuous ECG monitoring were implemented. The patient's rhythm did not improve despite intervention, and the patient went into asystole.
- Lessons Learned: This case emphasizes the need for careful assessment of the entire clinical picture when diagnosing agonal rhythms, especially in trauma patients where multiple factors can influence cardiac function.
Case Study 3: Successful Management of Agonal Rhythm
A 62-year-old male patient with a history of coronary artery disease presented with chest pain and rapidly evolving bradycardia that progressed to an agonal rhythm.
- Challenges: Rapid deterioration and the need for quick decision-making.
- Interventions: Immediate administration of atropine, transcutaneous pacing, and subsequent cardioversion proved effective in restoring a perfusing rhythm. The patient was later transferred to the cardiology unit for further management.
- Lessons Learned: This case demonstrates that while agonal rhythms often portend a poor prognosis, swift and appropriate intervention can, in some cases, improve outcomes.
Improving Agonal Rhythm Management:
- Advanced ECG interpretation training: Regular training and refreshers are essential for healthcare professionals.
- Prompt recognition and initiation of ACLS: Time is of the essence in managing these life-threatening rhythms.
- Teamwork and effective communication: A coordinated approach is crucial for optimal patient care.
Conclusion:
Agonal rhythms present a formidable challenge in emergency and critical care settings. These case studies illustrate the importance of accurate diagnosis, rapid intervention, and the need for a comprehensive understanding of underlying pathologies. By enhancing training and promoting collaborative care, healthcare providers can improve the management of agonal rhythms and potentially improve patient outcomes. Further research is vital to refine treatment strategies and improve survival rates associated with this critical arrhythmia. Learn more about advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) techniques to improve your skills in managing life-threatening rhythms. [Link to relevant resource or training].

Thank you for visiting our website wich cover about Case Studies: Recognizing And Managing Agonal Rhythms In Practice. We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and dont miss to bookmark.
Featured Posts
-
 Vendee Globe 2024 Le Cam Celebre Sa Victoire
Feb 05, 2025
Vendee Globe 2024 Le Cam Celebre Sa Victoire
Feb 05, 2025 -
 The Lyrical Themes In Amanda La Bollitas Hlb Discography
Feb 05, 2025
The Lyrical Themes In Amanda La Bollitas Hlb Discography
Feb 05, 2025 -
 Land A Pepsico Summer Internship E Commerce Focus 2025
Feb 05, 2025
Land A Pepsico Summer Internship E Commerce Focus 2025
Feb 05, 2025 -
 Rosa Parks Seat Reservation Returns To Metro Buses And Trains
Feb 05, 2025
Rosa Parks Seat Reservation Returns To Metro Buses And Trains
Feb 05, 2025 -
 La Wildfires Fuel A Grim Gambling Market
Feb 05, 2025
La Wildfires Fuel A Grim Gambling Market
Feb 05, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Used Cars In Fargo Craigslist Listings And Pricing
Feb 05, 2025
Used Cars In Fargo Craigslist Listings And Pricing
Feb 05, 2025 -
 Successions Shiv Roy Analyzing Her Moral Compass And Choices
Feb 05, 2025
Successions Shiv Roy Analyzing Her Moral Compass And Choices
Feb 05, 2025 -
 Understanding Turmeric And Dogs Health Benefits Risks And Safe Use
Feb 05, 2025
Understanding Turmeric And Dogs Health Benefits Risks And Safe Use
Feb 05, 2025 -
 What Time Is It In Boston Right Now A Quick Guide To Boston Time
Feb 05, 2025
What Time Is It In Boston Right Now A Quick Guide To Boston Time
Feb 05, 2025 -
 Court Appearance For Man Charged In Fentanyl Death Case
Feb 05, 2025
Court Appearance For Man Charged In Fentanyl Death Case
Feb 05, 2025
