Agonal Rhythm: Definition, Detection, And Clinical Significance
Agonal Rhythm: Definition, Detection, And Clinical Significance. Discover more detailed and exciting information on our website. Click the link below to start your adventure: Visit Best Website. Don't miss out!
Table of Contents
Agonal Rhythm: Definition, Detection, and Clinical Significance
Introduction:
The human heart, a tireless engine, can sometimes falter in its final moments. Understanding the subtle signs of impending cardiac arrest is crucial for medical professionals. One such sign, often overlooked, is agonal rhythm. This article delves into the definition, detection methods, and clinical significance of agonal rhythm, providing critical insights for healthcare providers and those interested in cardiology. We'll explore its implications for patient prognosis and the importance of rapid intervention.
What is Agonal Rhythm?
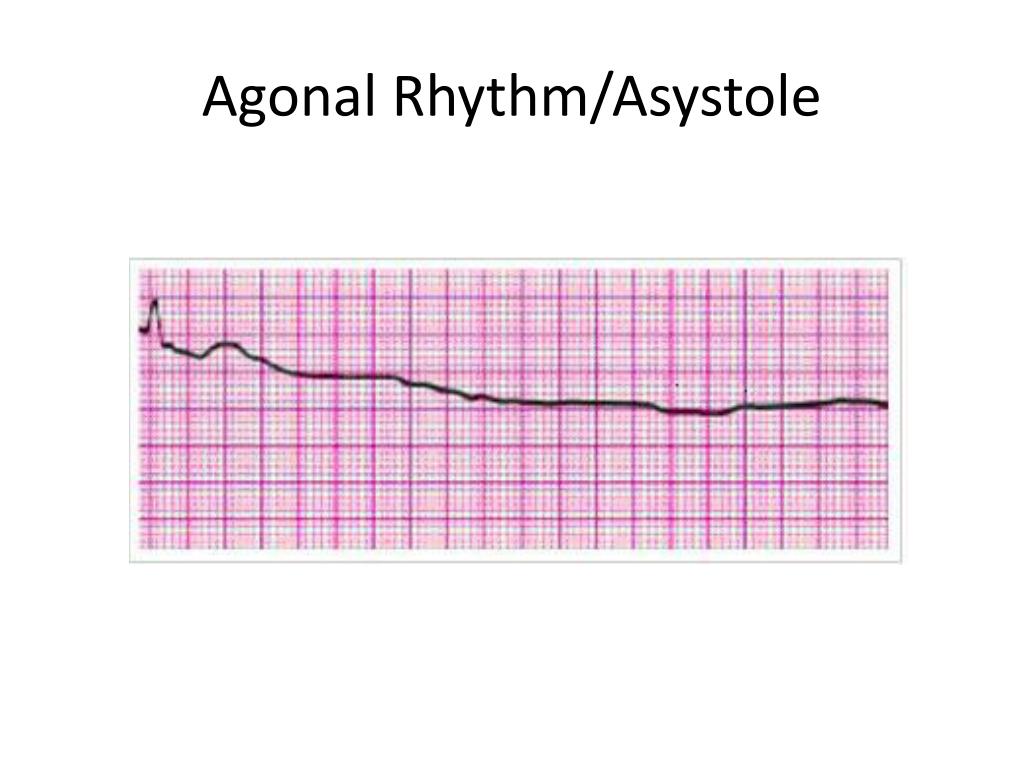
Agonal rhythm, also known as agonal gasping or agonal breathing, is a slow, irregular, and often ineffective heart rhythm occurring immediately before cardiac arrest. It's characterized by extremely slow heart rates (bradycardia) and irregular pulse patterns. Unlike other cardiac arrhythmias, agonal rhythm signifies the heart's imminent failure. This isn't a treatable rhythm itself, but rather a marker of extreme cardiac compromise. Understanding this crucial distinction is paramount.
Key Characteristics of Agonal Rhythm:
- Extremely slow heart rate: Rates significantly below 20 beats per minute are common.
- Irregular rhythm: The heartbeats are inconsistent in both timing and strength.
- Weak or absent pulse: Palpating a pulse may be difficult or impossible.
- Decreased or absent blood pressure: Systemic circulation is severely compromised.
- Often accompanied by agonal breathing: Gasping or irregular breathing patterns frequently occur simultaneously.
Detecting Agonal Rhythm:
Detecting agonal rhythm requires a multifaceted approach utilizing various diagnostic tools. Accurate and prompt detection is crucial for initiating immediate life-saving interventions.
Diagnostic Methods:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG provides the definitive diagnosis of agonal rhythm, showcasing the characteristically slow and irregular waveforms. This is the gold standard for detection.
- Pulse oximetry: While not directly diagnosing agonal rhythm, decreased oxygen saturation (SpO2) can be an indicator of the severe circulatory compromise associated with this condition.
- Physical examination: Observing absent or extremely weak pulses, coupled with gasping respirations, points towards the possibility of agonal rhythm. This necessitates immediate ECG monitoring.
- Cardiac monitoring: Continuous cardiac monitoring in critical care settings allows for early detection of changes that might precede agonal rhythm, potentially allowing for preemptive interventions.
Clinical Significance and Management:
The clinical significance of agonal rhythm cannot be overstated. It's a terminal rhythm indicating the heart is failing. Immediate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) are crucial.
Treatment and Prognosis:
- Immediate CPR: Chest compressions and rescue breaths are essential to maintain some level of circulation until other interventions can be implemented.
- Defibrillation: Defibrillation is generally ineffective for agonal rhythm as it's not a shockable rhythm.
- Advanced life support (ACLS): Administering medications like epinephrine, and potentially considering other advanced techniques, may be part of the ACLS protocol. However, the prognosis remains very poor.
- Prognosis: Agonal rhythm carries a grim prognosis, indicating the patient is very close to death. Successful resuscitation is rare.
Conclusion:
Agonal rhythm is a critical sign marking the final stages of cardiac arrest. Rapid recognition through ECG monitoring, coupled with immediate CPR and ACLS, is paramount, even though the chances of successful resuscitation are low. Further research into preemptive interventions and improved understanding of the underlying pathophysiology of agonal rhythm is vital to improving patient outcomes. For healthcare professionals, continuous learning and proficiency in advanced cardiac life support are critical to effectively manage these life-threatening situations. This knowledge empowers medical teams to offer the best possible care during these critical moments.

Thank you for visiting our website wich cover about Agonal Rhythm: Definition, Detection, And Clinical Significance. We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and dont miss to bookmark.
Featured Posts
-
 Exploring Troy Selwoods Transition From Afl To Vfl
Feb 05, 2025
Exploring Troy Selwoods Transition From Afl To Vfl
Feb 05, 2025 -
 Lutte Contre Le Fentanyl Trump Et Les Defis A Relever
Feb 05, 2025
Lutte Contre Le Fentanyl Trump Et Les Defis A Relever
Feb 05, 2025 -
 Newell Brands Shifts Production Mexico To Tennessee
Feb 05, 2025
Newell Brands Shifts Production Mexico To Tennessee
Feb 05, 2025 -
 Omnicef Discontinuation Understanding The Impact On Patients
Feb 05, 2025
Omnicef Discontinuation Understanding The Impact On Patients
Feb 05, 2025 -
 Neil Gaiman And Amanda Palmer A Detailed Look At The Ongoing Lawsuit
Feb 05, 2025
Neil Gaiman And Amanda Palmer A Detailed Look At The Ongoing Lawsuit
Feb 05, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Used Cars In Fargo Craigslist Listings And Pricing
Feb 05, 2025
Used Cars In Fargo Craigslist Listings And Pricing
Feb 05, 2025 -
 Successions Shiv Roy Analyzing Her Moral Compass And Choices
Feb 05, 2025
Successions Shiv Roy Analyzing Her Moral Compass And Choices
Feb 05, 2025 -
 Understanding Turmeric And Dogs Health Benefits Risks And Safe Use
Feb 05, 2025
Understanding Turmeric And Dogs Health Benefits Risks And Safe Use
Feb 05, 2025 -
 What Time Is It In Boston Right Now A Quick Guide To Boston Time
Feb 05, 2025
What Time Is It In Boston Right Now A Quick Guide To Boston Time
Feb 05, 2025 -
 Court Appearance For Man Charged In Fentanyl Death Case
Feb 05, 2025
Court Appearance For Man Charged In Fentanyl Death Case
Feb 05, 2025
